Although the traditional wet tailings pond has low cost and mature technology, it occupies a large area and seriously pollutes the surrounding environment. If a dam bursts, it may even endanger the lives of humans and animals. Dry tailings stacking can largely avoid such disasters. In addition, dry tailings discharge has the following significant advantages, which we will discuss together.

Xinhai Mining took over a lead-zinc tailings dry stacking project in Bulgaria in 2015. When we first came into contact with this project, we learned that the plant used wet stacking to handle tailings in the early stage, which saved a lot of costs and created great economic benefits.
However, as the scale of the concentrator gradually expanded, the amount of tailings increased, and the wet tailings pond had obvious problems, including unlimited expansion of land area, large amount of water waste, and even pollution to the surrounding environment. The economic cost of maintaining this huge tailings pond was also increasing year by year. It was not until then that the person in charge of the project realized the seriousness of the problem and hoped that Xinhai could help them carry out the tailings dry stacking transformation project to completely eliminate the adverse effects of wet tailings.

The customer's needs in this project mainly include the following aspects:
(1) Improve the discharge concentration of tailings treatment;
(2) Recycle most of the water resources and return them to the concentrator for recycling;
(3) Save the increasingly scarce water and land resources and achieve the expected benefits of the concentrator.
During the communication between the person in charge of the Xinhai project and the owner of the concentrator, the customer's needs were understood. The owner required to improve the discharge concentration of the tailings treatment and recycle most of the water resources, which would then be returned to the concentrator for recycling, saving the increasingly scarce water and land resources on site and achieving the expected benefits of the concentrator.
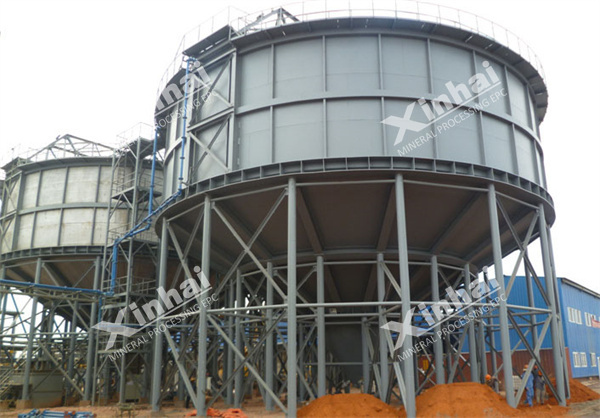
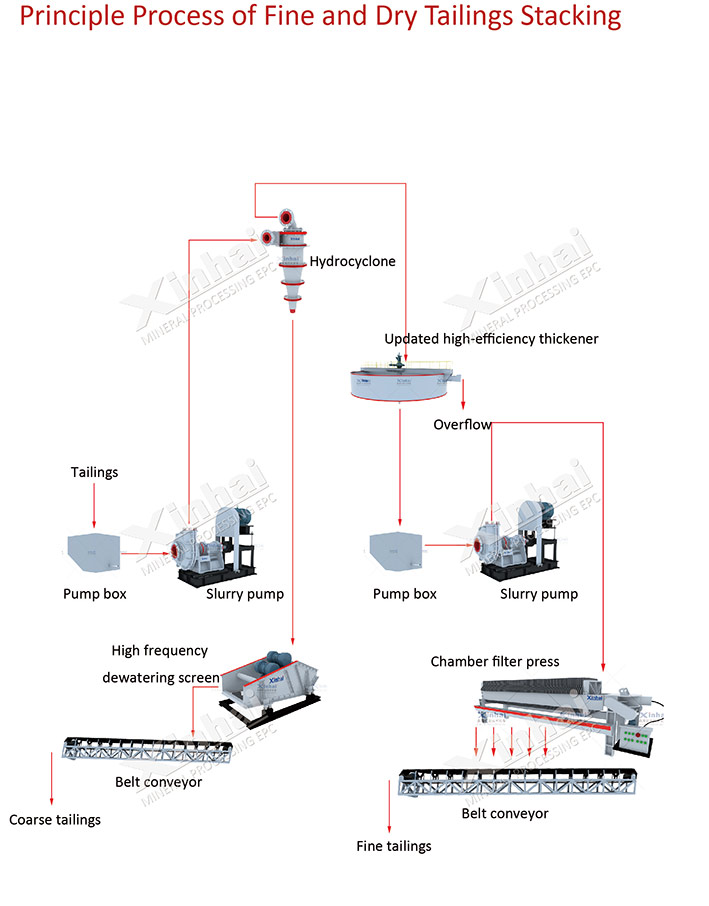
Before formulating the tailings dry stacking process, Xinhai Ore Dressing Laboratory took samples from the tailings pond and conducted a "supernatant solid content method to measure sedimentation velocity/compression concentration" sedimentation test and particle size analysis test. Based on the data shown in the test report, the tailings particle size, concentration, composition and mud content were analyzed. After investigation and continuous modification by Xinhai's professional and technical personnel, a tailings dry stacking process plan was formulated. The scope of the project construction drawing design is to build a new tailings dewatering workshop, using the following equipment:
(1) XCIIF600 hydrocyclone (2 sets), moisture content 60~70%;
(2) Φ18 high-efficiency deep cone concentrator (2 sets), moisture content 50%;
(3) filter press (2 sets), moisture content 9~12%;
(4) VD1536 high-efficiency multi-frequency dewatering screen (6 sets), moisture content 12~15%;
(5) wear-resistant slurry pump (4 sets).
In this tailings dry stacking project in Bulgaria, through the tailings dry stacking process developed by Xinhai, we achieved the following goals for our customers:
(1) Significantly reduce the water content of tailings: By adopting advanced tailings dry stacking technology, the project finally achieved the result of reducing the water content of tailings to less than 15%.
(2) Significantly improve the recycling rate of water resources: After the implementation of the project, 80% of the water can be recycled and returned to the concentrator for recycling.
(3) Effectively save the land area of the tailings pond: Through the application of tailings dry stacking technology, the land area of the tailings pond has been effectively saved. The saved land provides possibilities for the expansion of mining enterprises and the multifunctional use of land.
(4) Significantly reduce the daily management and maintenance costs of the tailings pond: The application of tailings dry stacking technology reduces the moisture content of the tailings pond, thereby reducing the daily management and maintenance costs of the tailings pond. This includes reducing the need for reinforcement, maintenance and monitoring of the tailings pond dam, as well as reducing environmental risks and related costs caused by improper moisture management.
(5) Reduce the pollution of the surrounding environment caused by tailings: The tailings dry stacking project effectively reduces the pollution of the surrounding environment caused by tailings by reducing the moisture content in the tailings. This includes reducing the risk of groundwater pollution caused by tailings pond leakage, and reducing the damage to the surrounding soil and vegetation caused by tailings ponds.
(6) Building a "green mine": The successful implementation of the project has enabled mining companies to take an important step in environmental protection and achieve the green transformation of mines. By reducing pollution, saving resources and improving efficiency, the project has helped companies establish a good social image and contributed to the realization of sustainable development goals.
(7) Improving the economic benefits of mining companies: The application of dry tailings stacking technology has not only been reflected in environmental and social benefits, but also brought significant improvements to companies in terms of economic benefits. By reducing water consumption, reducing land occupation and reducing operating costs, the overall economic benefits of companies have been enhanced.
It can be seen that wet tailings ponds seem to have low investment and high returns, but this is only a short-term benefit. In the long run, once the tailings stacking increases, water pollution and unlimited occupation of land resources will appear one by one. To completely solve these problems, dry tailings stacking is the best solution. If your tailings need to be reselected (recycled), dry stacking and other treatment needs, please contact us.