The phosphate ore flotation process is mainly divided into three processes: ore crushing, ore separation, and ore dehydration.
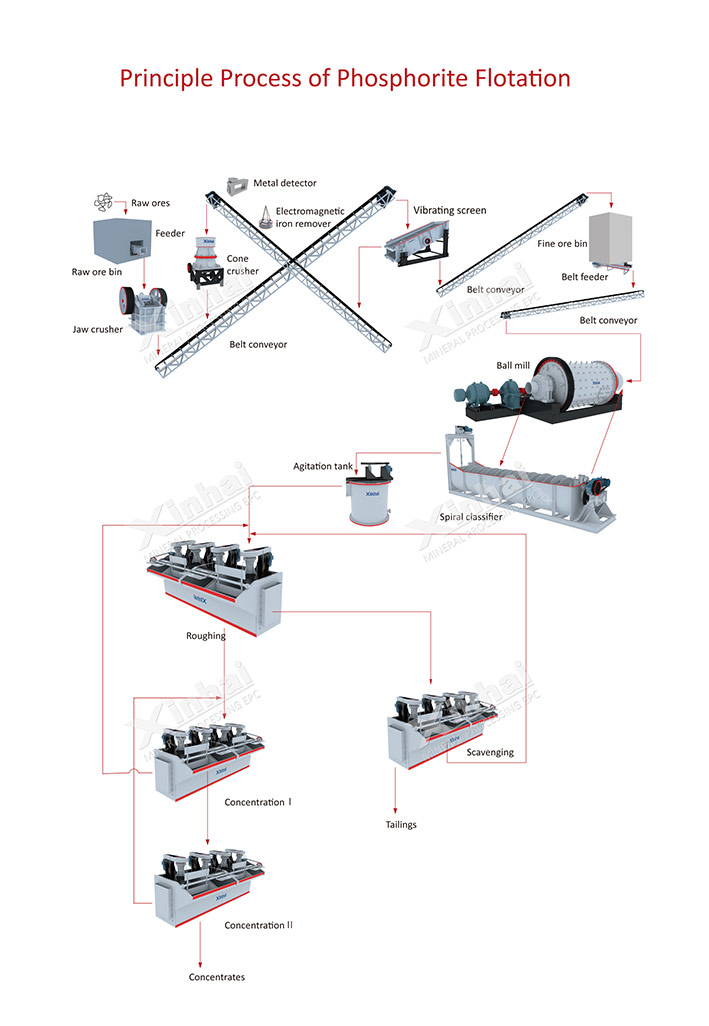
The process flow of phosphate rock crushing is: crushing → screening → grinding → classification.
Purpose of phosphate rock crushing: to separate the finely dispersed phosphate rock from other gangue particles and achieve monomer dissociation of the phosphate rock for subsequent separation processes.
Common phosphorus ore crushing process: three stages and one closed circuit crushing, that is, phosphorus ore undergoes coarse crushing, intermediate crushing, and one stage screening operations. One stage grinding refers to grinding the broken phosphate rock with a ball mill.
The phosphate ore separation process is mainly a flotation operation.
The phosphorus ore flotation process flow is as follows: first select the phosphorus ore and the recovered useful minerals by flotation, and then separate the phosphorus ore from the useful minerals. This method can save flotation reagents, reduce the number of flotation equipment, and reduce flotation costs.
Purpose of phosphate ore flotation: to achieve the enrichment of dissociated phosphate ores.
Common phosphate ore flotation processes include single reverse flotation, positive flotation, reverse flotation (positive and reverse flotation), and dual reverse flotation.
The purpose of phosphate concentrate dehydration is to make phosphate rock and other products easy to store and transport.
Phosphorus concentrate dehydration usually includes two processes: concentration and filtration. Phosphate ore is generally concentrated using a large concentration well (thickener), and filtering is typically performed using a disk filter.

The commonly used flotation processes for phosphate ore beneficiation include: positive flotation, reverse flotation, first positive then reverse flotation, first reverse then positive flotation, and dual reverse flotation processes.
Positive flotation of phosphate rock refers to adding collectors in the flotation process to enrich phosphate minerals in foam products, and at the same time using specific agents to inhibit gangue minerals such as silicate and carbonate in phosphate rock.
Scope of application: Suitable for siliceous or calcium-siliceous phosphorite, endogenetic apatite, and sedimentary phosphorus ore.
Process advantages: simple process, good impurity removal effect, and can effectively reduce the content of impurities such as Me and Fe. However, energy consumption is high and beneficiation costs are high.
Common flotation reagents: "S", "L", "sulfonated phenol tar", "F" series inhibitors, etc.
Phosphate ore reverse flotation refers to adjusting the pulp pH to a certain range (pH=4.0~5.0) with inorganic acid, enriching dolomite into foam products with specific collectors in weak acid medium, and keeping phosphorus minerals in the tank.
Scope of application: Suitable for processing the separation of phosphorus minerals and dolomite type gangue minerals. The elimination rate of dolomite type gangue minerals can reach 70% to 80%.
Process advantages: Without heating, it can be carried out at low temperature and normal temperature, reducing energy consumption and saving costs, but with weak applicability, mainly for calcareous phosphorus ores, with poor separation effect for siliceous phosphorus ores.
Common flotation reagents: inorganic acid regulators, modified fatty acid collectors, sulfated fatty acids, or additives added to their saponification process to improve their water solubility, temperature resistance, collection, and selectivity.
Positive flotation followed by reverse flotation refers to the use of inorganic alkali to adjust pulp to weak alkalinity, and the use of specific collectors to concentrate useful phosphorus minerals in foam products. Silicate gangue minerals are left in the tank for discharge, and foam is the positive flotation concentrate. Then, inorganic acids are added to adjust the pulp to a weak acidity. After the pulp preparation of the positive flotation concentrate (regrinding or non grinding), a collector is used to concentrate carbonate impurities, leaving useful phosphorus minerals in the tank to obtain a reverse flotation concentrate. The main purpose of reverse flotation is to remove MgO impurities from the phosphorus concentrate.
Scope of application: Processing siliceous calcium phosphate ores.
Process advantages: The phosphorus concentrate has a higher grade, and the combination of positive and negative flotation can effectively improve the processing performance of the phosphorus concentrate. However, the high cost of reagents has a significant impact on the recycling utilization of water resources in the concentrator.
Common flotation reagents: inorganic bases and inorganic acid regulators, XM-10, water glass, and sulfur phosphorus mixed acid inhibitors.
"Reverse to positive flotation of phosphate rock refers to the use of collectors to float carbonate gangue under acidic media conditions to obtain a reverse flotation concentrate, followed by two-stage grinding until siliceous gangue is hydrolyzed, and the flotation of phosphate minerals under alkaline media conditions to obtain a positive flotation concentrate.".
Scope of application: Low grade silicon-calcium collophanite.
Process advantages: No heating required, low energy consumption, but the circulating water needs to be treated separately, which has a significant impact on production.
The dual reverse flotation process for phosphate rock refers to using inorganic acids to adjust the pulp to a weak acidity, using fatty acid collectors to enrich a portion of dolomite gangue, and then enriching quartz minerals through fatty amine collectors. The phosphorus minerals in the tank are the final concentrate.
Scope of application: Processing mixed phosphorus ores with low content of siliceous gangue and carbonate. Especially for dolomite and quartz gangue minerals, the separation effect is better.
Process advantages: It can achieve low and normal temperature flotation, with simple process, low energy consumption, simple reagent system, and few reagent types. However, the amine collector used in this process is a cationic collector, which will produce a sticky foam with poor selectivity, and is more sensitive to slime. If the mud content in the raw ore is large, the desliming operation needs to be increased, which will make the process more complex.
Common flotation reagents: organic acid regulators, fatty acids, and fatty amine collectors.
The above is an introduction to the phosphate rock flotation process and the five commonly used flotation processes for phosphate rock flotation. The determination of any beneficiation scheme should be based on the results of beneficiation tests, with the goal of obtaining higher concentrate grades. Xinhai always adheres to the concept of "there are no identical two mines in the world", conducting targeted beneficiation tests on each batch of ore, ensuring the selection of optimal beneficiation processes, and ensuring the beneficiation recovery rate and concentrate grade.