According to the movement mode of materials during leaching, chemical leaching beneficiation methods can be divided into two types: percolation leaching and agitation leaching. Percolation leaching process is a commonly used beneficiation method when dealing with abandoned ore pillars, wall rocks, tailings and very low-grade minerals. Percolation leaching refers to a leaching method in which the leaching agent permeates through the fixed ore layer in a top-down or horizontal manner with the help of gravity or pressure. When using the percolation leaching method, selecting the appropriate percolation leaching method is the key to ensuring the economic benefits of the dressing plant. In this article, we will make an introduction of the six types of gold percolation leaching process from the selection of percolation leaching method and leaching agents.

Different mines adopt different percolation leaching methods. There are 3 leaching ways, namely, tank leaching (pool leaching), heap leaching and spot leaching. Under normal circumstances, for lean ore with small porosity, the tank leaching method can be selected. The ore needs to be crushed to less than 10 mm for tank leaching. While heap leaching is mostly used for ore mined or crushed to a certain particle size, such as mined waste rock with large porosity, sub-marginal ore and lean ore. The method of spot leaching is mostly used for the recovery of target minerals contained in underground mines developed by stage dilapidation method or residual ores and ore pillars in goafs.
1. Tank leaching method: According to the production processing volume, the shell of the leaching tank can be made of different materials. The size is based on the production design scale. In the actual production process, multiple percolation leaching tanks can be used for simultaneous operation. Under normal circumstances, it is necessary to set a false bottom at 0.1-0.2m of the bottom of the percolation leaching tank, and the false bottom is covered with permeable material, and then a thick layer of massive ore is laid on it. At the same time, in order to facilitate the flow of the leachate in the tank, the bottom can be slightly inclined towards the direction of the leachate outlet. Besides, you need to choose different types of tank linings based on ore properties and leaching liquid (various acids, alkalis and other leaching agents). The material of lining includes asphalt, acid-resistant concrete, lead plate, epoxy resin, polyethylene plastics, polymeric materials, etc.
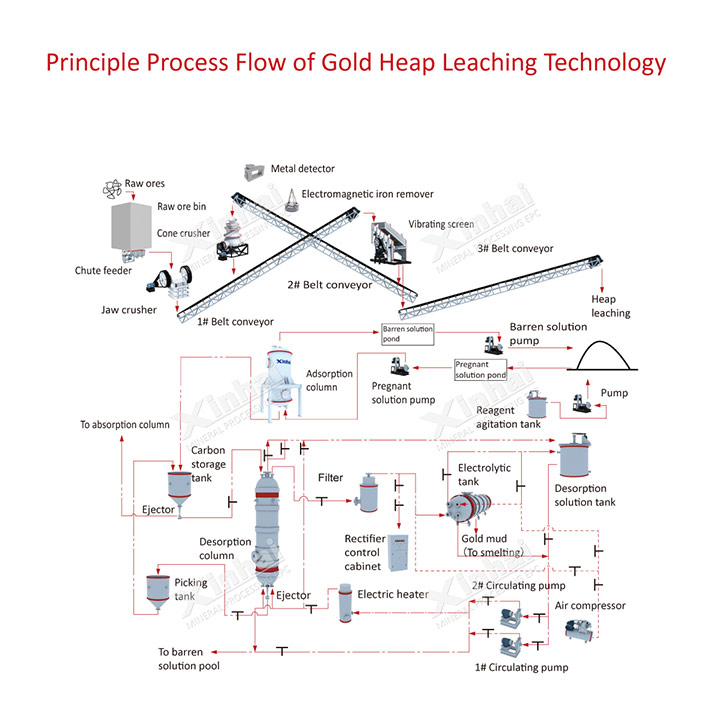
2. Heap leaching method: gold heap leaching is to mix fine ore particles with protective alkali (lime), stack them on the non-leakage ground (leaching pad), and extract gold from cyanide or non-toxic environmental-friendly agent. The solution of the agent is sprinkled on the ore heap. When the solution slowly passes through the ore heap (percolation) from top to bottom, the gold is dissolved, and the gold-containing solution (pregnant liquid) flowing out from the bottom is sent to carbon adsorption-desorption electrolysis , or zinc powder replacement and other processes to obtain gold mud, precious metals are obtained after smelting, and the cyanide solution or non-toxic gold leaching solution (lean solution) after gold removal is returned to the spray ore heap for recycling.
3. Spot leaching: spot leaching is to drill holes on the ground of the surveyed stope, and then inject the leaching agent into the ore body from the injection hole, and the leaching liquid is pumped from the recovery hole to the ground for treatment. Using the spot leaching method can reduce the production investment cost of expensive well construction, mining, transportation, grinding and other processes. At the same time, it can also reduce environmental pollution. However, spot leaching process has some limitations. It requires the ore body to have good permeability. Besides, there needs a corresponding impermeable layer around the ore body, stable bedrock and low groundwater level which prevents the outflow of the leaching liquid and facilitates the recovery of the leaching liquid. At present, spot leaching is mainly used to recover copper, uranium, rare earth, etc. from goafs. The clean water, acidic liquids, inorganic salts, etc. can be used as leaching agents.
Depending on the relative movement of the leaching material and leaching agent, co-current, counter-current and cross-current leaching can be selected. If the material to be leached and the leaching agent move in the same direction, it’s co-current. On the contrary, it is countercurrent. When the material to be leached and the leaching agent flow in a staggered direction, it is cross-current leaching. The percolation leaching tank can adopt the way of co-current, counter-current and cross-current. Heap leaching and in-site leaching generally use downstream leaching methods.

1. Co-current leaching: The content of the target components in the downstream leaching solution is higher, and the consumption of the leaching agent is smaller. But its leaching speed is small and the leaching time is long. In the production process, the co-current continuous leaching method can be adopted, in which the movement direction of the concentrate and the leaching agent is the same. Co-current continuous leaching is a process in which leaching agent, water and concentrate are continuously added to the reactor and discharged continuously. It has the advantages of large equipment production capacity, high heat utilization rate and low energy consumption.
2. Countercurrent leaching: Countercurrent leaching can make full use of the remaining leaching agent in the leaching solution, and obtain leaching solution with higher content of target components. Therefore, the leaching efficiency is high and the consumption of leaching agent is relatively low. However, this kind of process technology requires high operation control, and in the actual production process, it is mostly suitable for the leaching of low-grade concentrate.
3. Cross-current leaching: The leaching speed of cross-current leaching is fast, the leaching time is short, and the leaching rate is high. However, due to the large volume of the leaching solution and the high concentration of the remaining leaching agent in the leaching solution, a large amount of leaching agent needs to be consumed. The content of the target components in the cross-current leaching solution is relatively low. Nowadays, cross-current leaching method are mainly used for metal minerals of low-grade but high-value.